Managerial Economics
Managerial economics is a stream of management studies which emphasizes solving business problems and decision-making by applying the theories and principles of microeconomics and macroeconomics. cost accounting It is a specialized stream dealing with the organisation’s internal issues by using various economic theories.
Nature of Managerial Economics
To know more about managerial economics, we must know about its various characteristics. Let us read about the nature of this concept in the following points:
Art and Science: Managerial economics requires a lot of logical thinking and creative skills for decision making or problem-solving. It is also considered to be a stream of science by some economist claiming that it involves the application of different economic principles, techniques and methods, to solve business problems.
Micro Economics: In managerial economics, managers generally deal with the problems related to a particular organisation instead of the whole economy. Therefore it is considered to be a part of microeconomics.
Uses Macro Economics: A business functions in an external environment, i.e. it serves the market, which is a part of the economy as a whole.
Therefore, it is essential for managers to analyse the different factors of macroeconomics such as market conditions, economic reforms, government policies, etc. and their impact on the organisation.
Multi-disciplinary: It uses many tools and principles belonging to various disciplines such as accounting, finance, statistics, mathematics, production, operation research, human resource, marketing etc.
Prescriptive / Normative Discipline: It aims at goal achievement and deals with practical situations or problems by implementing corrective measures.
Management Oriented: It acts as a tool in the hands of managers to deal with business-related problems and uncertainties appropriately. It also provides for goal establishment, policy formulation and effective decision making.
Pragmatic: It is a practical and logical approach towards the day to day business problems.
Types of Managerial Economics
All managers take the concept of managerial economics differently. Some may be more focused on customer’s satisfaction while others may prioritize efficient production.
Scope of Managerial Economics
Managerial economics is widely applied in organizations to deal with different business issues. Both the micro and macroeconomics equally impact the business and its functioning.
Micro-Economics Applied to Operational Issues
To resolve the organisation’s internal issues arising in business operations, the various theories or principles of microeconomics applied are as follows:
- Theory of Demand: The demand theory emphasizes on the consumer’s behaviour towards a product or service. It takes into consideration the needs, wants, preferences and requirement of the consumers to enhance the production process.
- Theory of Production and Production Decisions: This theory is majorly concerned with the volume of production, process, capital and labour required, cost involved, etc. It aims at maximizing the output to meet the customer’s demand.
- Pricing Theory and Analysis of marketing structure It focuses on the price determination of a product keeping in mind the competitors, market conditions, cost of production, maximization sales volume, etc.
- Profit Analysis and Management: The organisations work for a profit. Therefore they always aim at profit maximization. It depends upon the market demand, cost of input, competition level, etc.
- Theory of Capital and Investment Decisions: Capital is the most critical factor of business. This theory prevails the proper allocation of the organisation’s capital and making investment in profitable projects or venture to improve organisational efficiency.
Macro-Economics Applied to Business Environment
Any organisation is much affected by the environment it operates in. The business environment can be classified as follows:
- Economic Environment: The economic conditions of a country, GDP, economic policies, etc. indirectly impacts the business and its operations.
- Social Environment: The society in which the organisation functions also affects it like employment conditions, trade unions, consumer cooperatives, etc.
- Political Environment: The political structure of a country, whether authoritarian or democratic; political stability; and attitude towards the private sector, influence organizational growth and development.
Managerial economics provides an essential tool for determining the business goals and targets, the actual position of the organization, and what the management should do fill the gap between the two.
Henri Fayol’s 14 Principles of Management
Though these principles are not very appropriate for the modern business world, they have laid the foundation of business management.
Also, they are studied and used by many researchers, experts and entrepreneurs, even today.
What are the Principles of Management?
The principles of management refer to the fundamental truth which is generally applied to the everyday business operations for ensuring effective management of the organization.
Features of Principles of Management
The principles of management are identified facts which are developed through individual experiences and can be applied to all kinds of business entities. To know more about these principles, let us go through its following characteristics: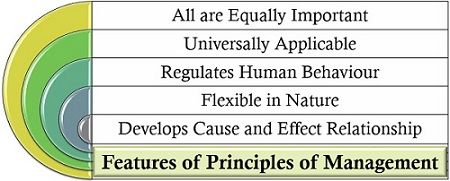
- All are Equally Important: Every management principle holds equal importance in the business organization.
- Universally Applicable: These principles can be applied to any kind of organization, whether large or small or belongs to any industry.
- Regulates Human Behavior: The application of the management principles helps the organization to monitor and control the behaviour of the personnel.
- Flexible in Nature: The applicability of these principles vary from organization to organization.
- Develops Cause and Effect Relationship: The principles of management establishes a relationship between every action and its consequences in the short and long run.
Administrative Management and Henri Fayol
The concept of the administrative management stating the 14 principles of management was given by Henry Fayol (1841-1925) in his book published in the year 1916 under the name ‘General and Industrial Management‘.
Administrative Management and Henri Fayol
The concept of the administrative management stating the 14 principles of management was given by Henry Fayol (1841-1925) in his book published in the year 1916 under the name ‘General and Industrial Management‘
Administrative Management and Henri Fayol
The concept of the administrative management stating the 14 principles of management was given by Henry Fayol (1841-1925) in his book published in the year 1916 under the name ‘General and Industrial Management"
These principles have laid the foundation of what it is called modern management theory today. This theory is still applied by some of the famous companies like Apple, Google, Microsoft, etc. He is therefore known as the ‘father of modern management theory’.
Fayol worked for an iron and coal company named, ‘Commentry-Fourchambault‘ in France for 58 years, where he was a mining engineer in the initial years and lastly became the CEO of the company.
He gained ample understanding of the problems at all levels of the organization during his growth tenure.
Thus, through all his experience and learning, he developed the 14 principles for superior management of any organization.
Henry Fayol has himself followed these principles throughout his management career. Therefore, his motive was to provide a guideline to all the other managers for the efficient management of their organizations.
Fayol’s 6 Activities of Industry
In his concept of administrative management, Fayol stated that there are six significant activities which are performed in every type of organization. These activities comprise of: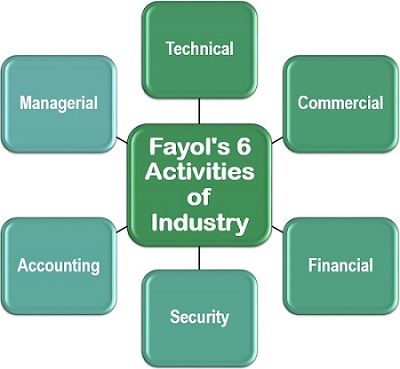
- Technical: The technical part includes product or process engineering and production of goods or services.
- Commercial: All the marketing functions, including procurement, sales, distribution and promotion, are a part of commercial activity.
- Financial: The financial activity consists of the acquisition of capital and its management.
- Security: The protection and safety of the resources, i.e., personnel, capital and assets, comes under security.
- Accounting: The accounting activity comprises of bookkeeping, record maintenance, reporting, cost accounting inventory management, etc.
- Managerial: Managerial activity includes the various functions of management, i.e., planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating and controlling of the business operations.
Fayol’s 6 Functions of Management
Henry Fayol gave six managerial functions, which are performed in almost every organization. Therefore we can say that these functions are universally applicable. Let us now understand each of these in detail below: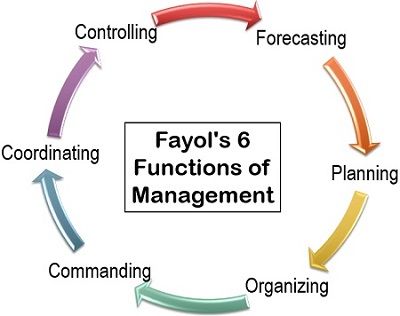
- Forecasting: The first function is to analyze the present and past information to predict the future and plan accordingly.
- Planning: The top management plans a suitable course of action, based on the business forecast.
- Organizing: The management next needs to systematically arrange the resources, i.e., raw material, capital and human resource as per the planning.
- Commanding: The managers give instructions, directions and orders to the subordinates in this function.
- Coordinating: In this function, the management should ensure proper synchronization among all the departments. For this purpose, weekly meetings can be held with the managers of all the departments.
- Controlling: The managers need to evaluate the performance of the personnel by establishing the standards, comparing the actual performance with the desired one and implement the corrective measures accordingly.
14 Principles of Management by Henri Fayol
The term ‘principles of management’ sounds quite complicated; however, it is merely a set of fundamental truth for effectively and efficiently managing any business organization.
Fayol developed these principles on the grounds of his findings and experience, which he gained throughout his journey in an iron and coal company.
We will now learn about each of these 14 principles in the following description: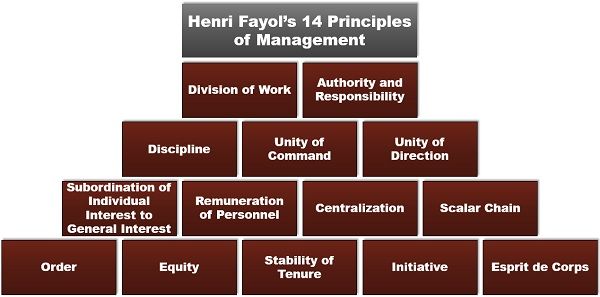
Division of Work
The first principle emphasizes on dividing the work into smaller tasks which can be equally allotted to individual employees based on their ability, skills and specialization. This is to enhance their overall efficiency in performing their respective duties.
Authority and Responsibility
Giving of responsibility is always accompanied by the delegation of a certain level of authority to fulfil the given task efficiently.
Responsibility without authority may result in improper utilization of the provided resources or delay in task accomplishment. Whereas, power without responsibility may result in reckless attitude and poor leadership.
Discipline
The management must ensure that employees abide by the rules, norms, principles and policies of the organization to maintain a disciplined work environment.
The managers can adopt the techniques of motivation and penalty (in case of non-compliance) for this purpose.
Unity of Command
This principle states that every employee should be headed by only one manager and not by two or three senior authorities.
It creates a lot of confusion for the employee and may lead to conflict among the instructing supervisors or managers.
Unity of Direction
The efforts and individual objectives of all the employees performing various tasks should be directed towards the attainment of the organizational goals as an ultimate aim.
Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interest
The management should understand the individual objectives of each employee so that these personal interest of the employees can be aligned with the organizational interest or purpose.
This principle says that the organization’s goal is superior to the individual aim of the employees.
Remuneration of Personnel
The remuneration policy (i.e., payment of wages and salary) of the employer should be fair enough. This is to ensure employee satisfaction, and it should either match or exceed the remuneration provided by the competitors.
centralization
The level to which the authority of decision-making is delegated to the subordinates depends upon the organization’s size, type, nature and situation.
Usually, the large companies require decentralization however, small firms may carry on with a centralized approach.
Scalar Chain
The organizational structure should be such that the employees can follow a clear hierarchy. Thus, everyone knows to whom they are accountable and, a smooth flow of information can be maintained from top to bottom level and vice-versa.
However, in case of an emergency or situation demanding quick decision-making, this concept may create a hurdle.
Therefore, for such circumstances, Fayol has given the idea of ‘gangplank’. That is, an employee at any level can break the scalar chain and communicate with the other employee belonging to any authority level.
Order
Here, order refers to organizing everything (i.e., all the resources) in a systematic and planned manner.
In short, every object should have a pre-decided place, and every employee must be placed in the right role or job position.
Equity
According to Fayol, the management should never discriminate between the employees and treat them as equal in all respect.
If the organization is impartial towards its staff, they too tend to develop trust and belongingness towards the company.
Stability of Tenure
This principle is related to the retention and attrition of employees.
The growth of any business depends upon its ability to retain its employees for a long-term since recruitment, selection and training of new personnel involves enormous cost and time.
Initiative
The organization must encourage and inspire its employees to give their input and take the initiative in the execution of the planned activity.
It not only brings out innovative and creative ideas but also motivates the employees to perform their best.
Esprit de Corps
Teamwork is an essential part of any business, and therefore, the organization should ensure that there is a cordial relation among the employees.
It develops a unity, team spirit, loyalty, mutual understanding and positive work environment in the organization.
Limitations of Fayol’s Principles of Management
Later on, Fayol’s 14 principles of management were criticized by many management critics. To know the reasons for this criticism, read below:
Fayol’s principles revolve around catering to the needs of the organization; however, customer needs and demand are entirely ignored in this approach.
These principles are not based on practical research; instead, Fayol gave this concept as per his personal experience.
The 14 principles of management were developed in the period 1900s when the business scenario was very different from today. Therefore these are not exactly suitable for the present era and needs modification.





Nice blog. Good study Thanks for sharing the valuable content.
ReplyDeleteModern Group of Institutes Indore